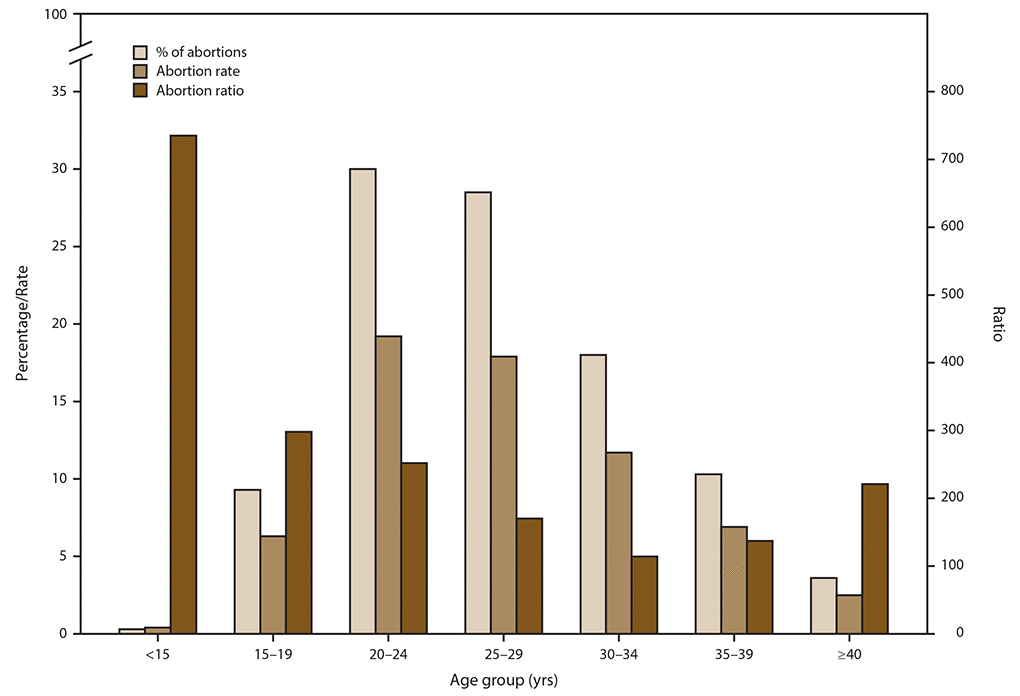
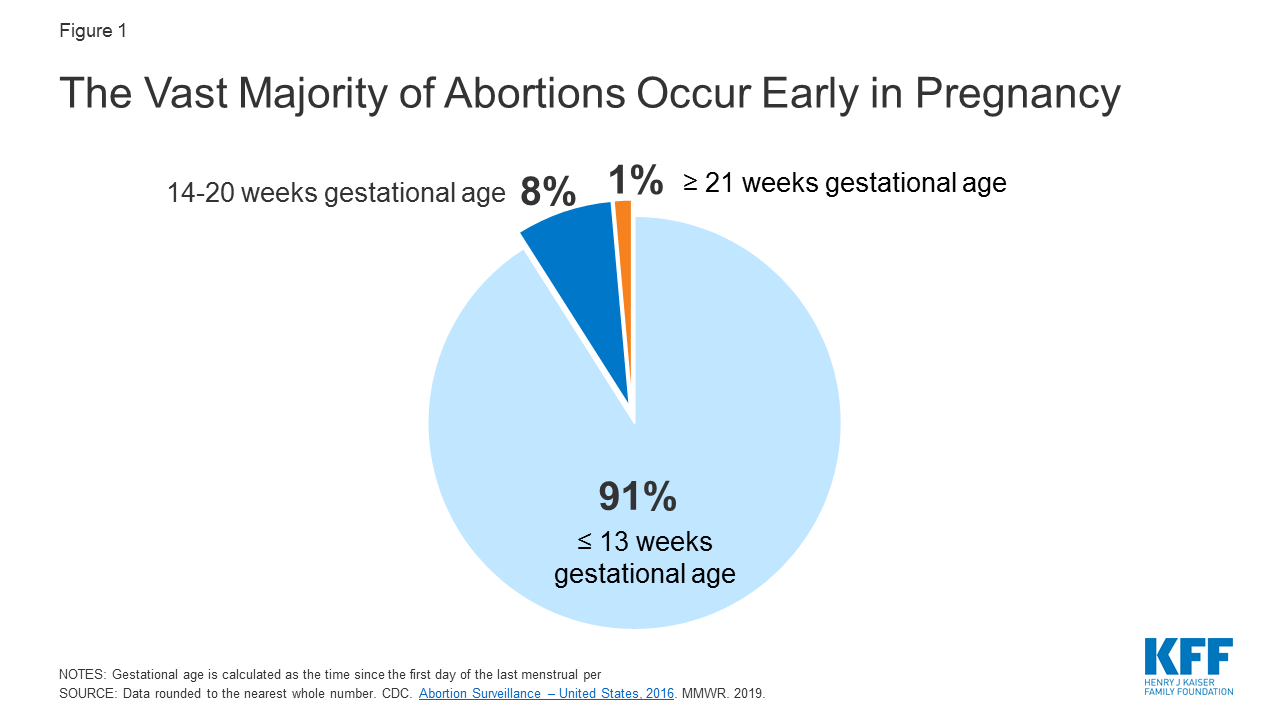
The amygdalathat pesky corner of the brain that produces feelings of anxiety fear and general stressis physically smaller in the brains of expert meditators. When neuroscientists tested expert meditators they discovered something surprising.
 Altered Traits Science Reveals How Meditation Changes Your Mind Brain And Body Goleman Daniel Davidson Richard J 9780399184390 Amazon Com Books
Altered Traits Science Reveals How Meditation Changes Your Mind Brain And Body Goleman Daniel Davidson Richard J 9780399184390 Amazon Com Books
Researcher Catherine Kerr found that people who practiced mindful meditation were able to adjust the brain wave that screens out distractions and.

Meditation brain changes. Mindfulness meditation alters regions of the brain associated with memory awareness of self and compassion according to a brain imaging study by researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston and the University of Massachusetts Medical School in Worcester. Different parts of the brain get stimulated in a particular manner during meditation. It changes for the better in your brain giving you a more positive outlook on yourself and your life.
Amygdala There is another area of the brain that is changed through meditation. It is considered to be the most evolved part of the brain and meditation tends to make this part of the brain go offline. Specifically the science behind how your brain changes the longer you meditate.
In 2011 Sara Lazar and her team at Harvard found that mindfulness meditation can actually change the structure of the brain. Daniel Goleman and Richard Davidson tell the story of this revolutionary breakthrough in our understanding of how meditation works. The effect of Buddhist meditation isnt just momentary.
Davidson adds that research on neuroplasticity gives neuroscientists a framework for tracking meditation research. It can alter deep-seated traits in our brain patterns and character. General-led study shows changes over time in areas associated with awareness empathy stress Participating in an 8-week mindfulness meditation program appears to make measurable changes in brain regions associated with memory sense of self empathy and stress.
Research has shown that there are several ways that meditation can change the brains structure and function. Science has discovered a powerful connection between meditation and brain health. Meditation when done correctly can move the brain waves from a higher frequency to a lower frequency thereby having the ability to change how you feel.
Thisin a tiny nutshellis how meditation changes your brainand your life. Meditation changes brain connectivity in the parts of Cerebral Cortex the biggest part and outer wrinkled layer of the brain. This area of the brain is responsible for rational.
It has also been found to increase feelings of kindness and empathy. Through mindfulness and other practices of meditation research shows meditators can effectively reverse the trend of decline and actually increase their brain cells gray matter. I think this is important for many reasons but one of the most salient is that this information serves as a great.
And CIHM is beginning to see that even short amounts of practice like 30 minutes of meditation per day can induce measurable changes in. Other studies have found differences in the brains of experienced meditators compared with non-meditators but this is the. Meditation is like a vitamin for your brain because it helps with things like anxiety frustration self-acceptance optimism and loneliness.
But it doesnt get larger. Enlarges the prefrontal cortex. A report of the study from the Harvard Gazette published in.
Meditation in general has been shown to actually beef up parts of the brain connected to happiness and shrink parts of the brain connected to stress and repetitive unpleasant emotions. This new research found measurable changes in the brain after an eight-week program. Meditation can change where activity occurs in our brains.
The frontal lobe in particular is the part of the brain that is responsible for reasoning planning emotions and self-conscious awareness. Cerebral Cortex is involved in sight hearing smell and sensation emotions executive functions such as cognitive thinking planning and memory.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/nexplanon-birth-control-implant-faq-9068641-5c8ad59046e0fb00014a9688.png)