I magine 100 people are ill with Covid-19. Columnist Ed Tobias shares the results of a study that found significant variance in efficacy of a COVID-19 vaccine depending on DMT use.
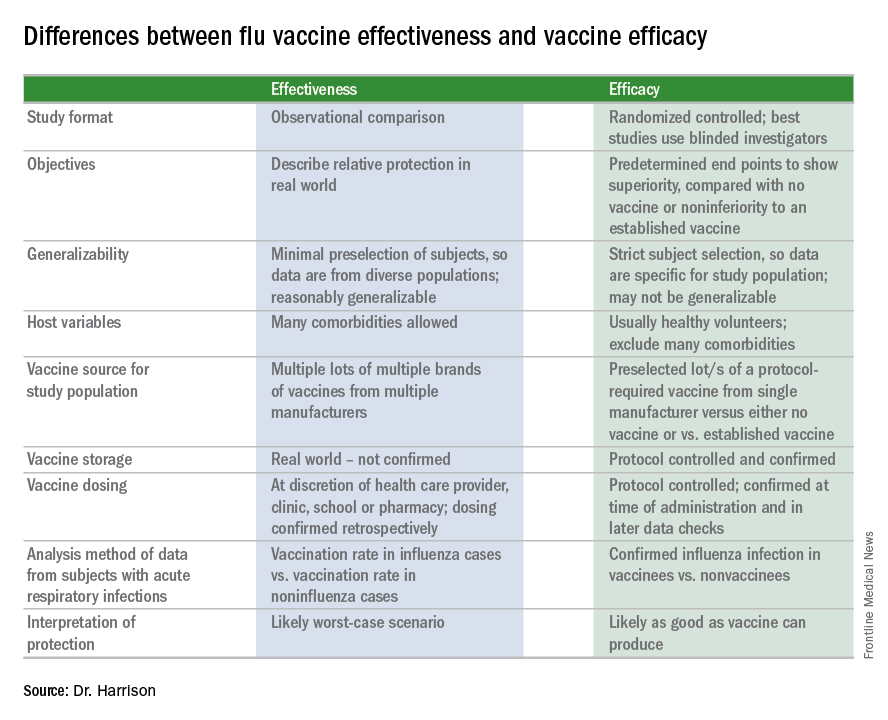 Vaccines Effectiveness Vs Efficacy Chest Physician
Vaccines Effectiveness Vs Efficacy Chest Physician
Sometimes vaccines may have to undergo Phase IV trials after the vaccine is approved and licensed.

What is vaccine efficacy. Vaccines dont protect only the people who get them. Vaccine efficacy is the percentage reduction in a disease in a group of people who received a vaccination in a clinical trial. Vaccine efficacy is the.
Across all age groups as cumulative vaccine coverage increased the 7. It means that in a population such as the one enrolled in the trials with a cumulated COVID-19 attack rate over a period of 3 months of about 1 without a vaccine we would. In Phase III the vaccine is given to thousands of people and tested for efficacy and safety.
Those people are broken into two groups. The estimates of vaccine efficacy against all SARS-CoV-2 outcomes were higher than 96 among people aged 75 years and older. For example there were 43.
For statisticians efficacy is a measurement of how much a vaccine lowers the risk of an outcome. For the four vaccine candidates now in phase III trials in the United States the primary goal is not necessarily to stop. Half get the vaccine and half get a placebo then theyre sent out to live their lives while scientists monitor whether or not they get COVID-19 over several months in the trial for Pfizer biotech.
COVID vaccines developed by PfizerBioNTech as well as by those by Moderna were less efficient against the double mutant virus discovered in India. A vaccines efficacy at preventing an exposed person from. What is vaccine efficacy.
Lets say for example that. Efficacy is a measure of relative reduction in risk says Natalie Dean a biostatistician specializing in infectious-disease epidemiology at the University of Florida. Vaccines were shown to have 9495 efficacy in preventing symptomatic COVID-19 calculated as 100 1 minus the attack rate with vaccine divided by the attack rate with placebo.
Efficacy specifically applies to how a vaccine works in a clinical trial. For example Johnson Johnson observed how many people who received a vaccine nevertheless got. 90 efficacy means if only theyd had the vaccine on average only 10 would have got ill.
It differs from vaccine effectiveness which. Vaccination works very well to prevent both symptoms and severe disease in the short to medium term but efficacy is predicted to decline over the first few months for most of these vaccines. Vaccine efficacy is expressed as a proportionate reduction in disease attack rate AR between the unvaccinated ARU and vaccinated ARV groups under the phase III trial.
Vaccine efficacy is the relative reduction in the risk. As the B1617 lineage continues to jump international borders the World Health Organisation WHO stressed that there was a limited reduction in the. A vaccines efficacy rate is calculated in large clinical trials when the vaccine is tested on tens of thousands of people.
It is measured during the Phase III period. 12 Zeilen Prevention of severe disease. Efficacy refers to the difference between the people who fell sick after vaccination and those who fell sick without it.
Whatever your risk was before it is reduced by 90 per cent if you get vaccinated. From efficacy immunity and side-effects while the three approved vaccines for use carry good benefits in mitigating the risks of the harmful coronavirus there are some noteworthy differences as. Read more about Scientists find new way of predicting Covid vaccine efficacy against virus on Business Standard.
Because they slow the spread of the virus they can over time also drive down new infection rates and protect society as a whole. The early immune response in a person who has been vaccinated for Covid-19 can predict the level of protection they will have to the virus over time according to an analysis.